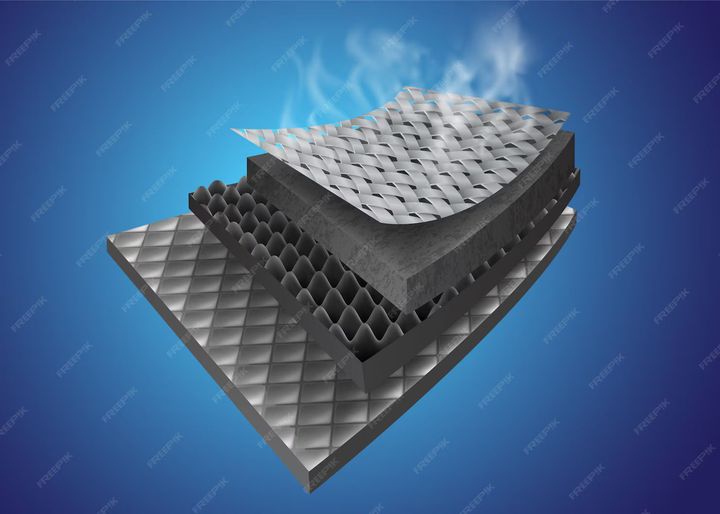
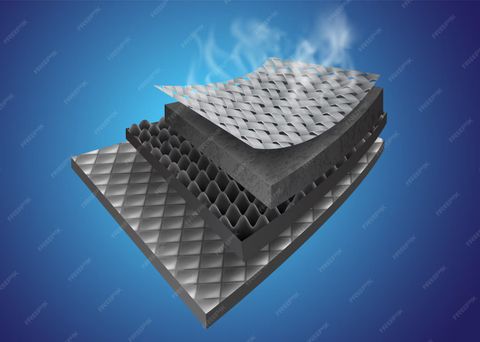
These materials exist to improve energy efficiency, enhance comfort, and support building performance. In residential, commercial, and industrial settings, insulation plays a critical role in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC efficiency). By minimizing temperature fluctuations, insulation contributes to reduced energy consumption and improved indoor environmental quality.
Common thermal insulation materials include:
-
Fiberglass insulation
-
Mineral wool (rock wool and slag wool)
-
Expanded polystyrene (EPS)
-
Extruded polystyrene (XPS)
-
Polyurethane foam
-
Cellulose insulation
-
Aerogel insulation panels
Each material has unique thermal conductivity values, often measured as R-value (thermal resistance). A higher R-value indicates stronger resistance to heat flow.
Below is a simplified comparison of common insulation materials:
| Material | Typical R-Value (per inch) | Fire Resistance | Moisture Resistance |
|---|
| Fiberglass | 2.2 – 2.7 | Moderate | Moderate |
| Mineral Wool | 3.0 – 3.3 | High | High |
| EPS | 3.6 – 4.0 | Moderate | Moderate |
| XPS | 4.5 – 5.0 | Moderate | High |
| Polyurethane Foam | 5.5 – 6.5 | Varies | High |
This data supports building material selection based on climate, building codes, and project requirements.
Why Thermal Insulation Materials Matter Today
Energy efficiency has become a major global priority. Rising energy demand, increasing electricity tariffs, and climate change concerns have made building performance a key focus in construction and infrastructure development.
Thermal insulation materials affect:
-
Homeowners seeking lower energy bills
-
Commercial property developers
-
Industrial facility managers
-
Architects and civil engineers
-
Sustainability consultants
Insulation reduces heating and cooling loads, which directly improves HVAC system performance. This lowers carbon emissions and supports green building certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM.
In warm climates, insulation helps prevent heat gain. In colder regions, it prevents heat loss. Both scenarios contribute to improved thermal comfort and indoor air quality.
Key problems solved by thermal insulation materials include:
-
Excessive energy consumption
-
Indoor temperature instability
-
Condensation and moisture damage
-
Noise transfer in buildings
-
High greenhouse gas emissions
Energy-efficient construction is now linked to property valuation and long-term asset performance. High-performance insulation systems are increasingly integrated into smart building technologies and sustainable construction frameworks.
Recent Updates and Trends in 2025
Over the past year, several developments have influenced the insulation market and energy-efficient construction practices.
In 2025, there has been growing adoption of low-global-warming-potential (GWP) insulation materials. Manufacturers are developing products with reduced environmental impact, especially in foam insulation segments. Regulatory shifts toward climate-neutral construction have accelerated research in advanced materials such as aerogels and vacuum insulation panels.
Digital energy modeling tools have become more widely used in 2025. Building Information Modeling (BIM) software now integrates insulation performance simulations, helping architects analyze thermal bridges before construction begins.
Key 2025 trends include:
-
Increased demand for net-zero energy buildings
-
Greater use of recycled and bio-based insulation materials
-
Stronger building envelope standards in new developments
-
Integration of insulation with smart sensors for monitoring thermal performance
Global infrastructure investments and urban housing initiatives in early 2025 have also expanded insulation demand in emerging markets. This growth is closely linked to energy efficiency regulations and climate adaptation strategies.
Laws, Regulations, and Government Policies
Thermal insulation materials are regulated by building codes and energy performance standards in many countries.
In India, the Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) sets minimum energy efficiency requirements for commercial buildings. It includes specific guidelines for wall insulation, roof insulation, and thermal transmittance (U-value) limits.
Other global regulatory frameworks include:
-
International Energy Conservation Code (IECC)
-
European Union Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD)
-
ASHRAE Standard 90.1 for energy-efficient buildings
These policies require:
-
Minimum R-values for walls and roofs
-
Air sealing standards
-
Thermal bridge reduction strategies
-
Energy performance certifications
Government programs often encourage energy-efficient retrofitting of existing buildings. Such initiatives focus on reducing national energy consumption and achieving climate targets.
Compliance with insulation standards ensures building safety, fire resistance, and structural performance. Fire classification, smoke development ratings, and material safety standards are also part of regulatory evaluation.
Tools and Resources for Thermal Insulation Planning
Several tools and digital platforms help professionals and property owners evaluate insulation needs.
Useful tools include:
-
R-Value Calculators for estimating thermal resistance
-
U-Value Calculators for measuring heat transfer rates
-
Building Energy Simulation Software such as EnergyPlus
-
BIM Platforms like Autodesk Revit
-
Government energy efficiency portals
-
ASHRAE and ECBC documentation resources
Online climate zone maps assist in selecting appropriate insulation thickness based on regional temperature patterns.
Below is a simplified representation of how insulation reduces heat flow:
Heat Flow Without Insulation
This visual comparison shows reduced heat transfer when insulation is applied effectively.
Professionals also use infrared thermography to detect thermal leaks and evaluate insulation performance in existing buildings.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main purpose of thermal insulation materials?
Thermal insulation materials reduce heat transfer between indoor and outdoor environments. They help maintain comfortable indoor temperatures and improve energy efficiency.
How is insulation performance measured?
Insulation performance is measured using R-value and U-value. R-value indicates resistance to heat flow, while U-value measures how much heat passes through a structure.
Which insulation material has the highest R-value?
Polyurethane foam generally has one of the highest R-values per inch among commonly used insulation materials. However, the appropriate choice depends on project needs, climate, and regulations.
Are thermal insulation materials environmentally friendly?
Some insulation materials are produced using recycled content or bio-based fibers. In 2025, there is increased focus on materials with lower environmental impact and reduced global warming potential.
Does insulation help reduce carbon emissions?
Yes. By lowering energy consumption for heating and cooling, insulation indirectly reduces greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation and fossil fuel use.
Conclusion
Thermal insulation materials are fundamental to modern construction and energy-efficient building design. They regulate indoor temperatures, enhance comfort, and reduce energy consumption across residential, commercial, and industrial structures.
With growing attention to climate change, building regulations, and sustainable development goals, insulation technologies continue to evolve. Advanced materials, stricter building codes, and digital energy modeling tools are shaping the future of thermal performance in 2025.
Understanding insulation types, regulatory requirements, and available tools allows informed decision-making in construction and renovation projects. As global energy standards become more demanding, thermal insulation remains a critical component of sustainable infrastructure and high-performance building envelopes.