Car Body Welding Robots Guide to Automation and Smart Manufacturing
Car body welding robots are advanced robotic welding systems used in automotive manufacturing to join metal components of vehicle frames and body structures. These industrial automation machines operate with programmed precision, using technologies such as robotic arms, welding torches, sensors, and software control systems. They exist to improve consistency, production speed, and workplace safety in large-scale vehicle assembly plants.
In modern smart factory environments, car body welding robots are part of automated production lines. They handle repetitive and high-heat welding tasks that require accuracy at the millimeter level. By reducing human exposure to sparks, fumes, and extreme temperatures, they help create safer industrial workplaces while maintaining quality standards.
What Are Car Body Welding Robots and Why They Exist
Car body welding robots are programmable robotic arms designed to perform spot welding, arc welding, laser welding, and other joining processes in vehicle production. These robots are typically installed along automated assembly lines where car frames, doors, and panels are positioned by conveyor systems.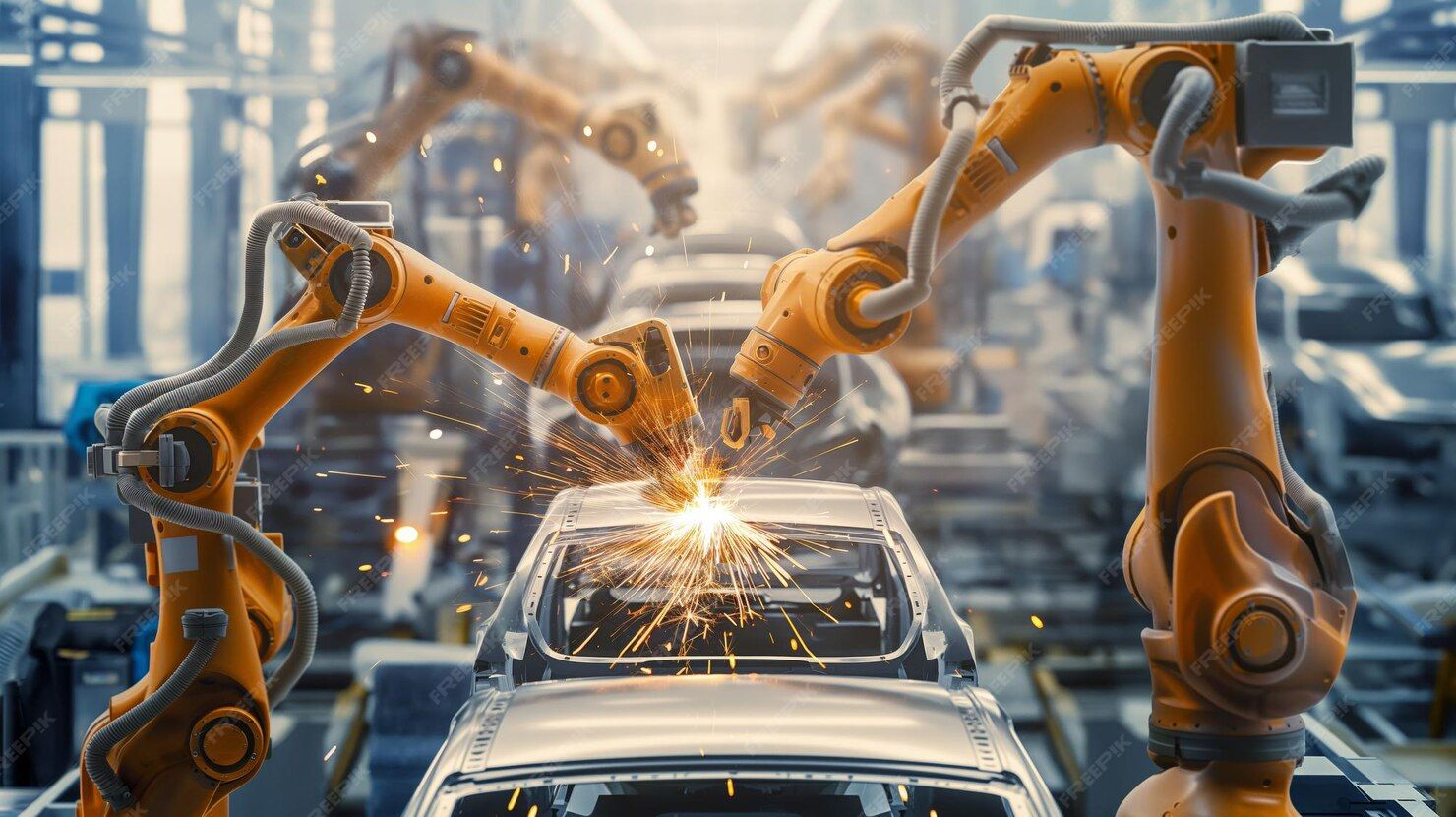
They exist primarily to address key manufacturing challenges:
-
Maintaining consistent weld quality
-
Reducing human error in repetitive processes
-
Increasing production speed
-
Supporting high-volume automotive output
-
Enhancing worker safety in hazardous environments
Automotive welding requires structural integrity because the welded joints directly affect vehicle strength and crash performance. Robotic welding systems ensure each weld meets predefined standards set by automotive engineering guidelines.
Why Car Body Welding Robots Matter Today
The automotive industry is undergoing rapid transformation driven by electric vehicles, smart manufacturing, and advanced robotics. Car body welding robots play a critical role in this shift.
They matter today because:
-
Electric vehicle platforms require redesigned body structures
-
Lightweight materials such as high-strength steel and aluminum demand precise welding
-
Global competition pushes manufacturers to improve efficiency
-
Workplace safety standards are becoming stricter
-
Industry 4.0 initiatives emphasize automation and data analytics
Car body welding robots affect:
-
Automotive manufacturers
-
Robotics engineers
-
Industrial automation specialists
-
Safety compliance professionals
-
Supply chain and production managers
By solving production bottlenecks and ensuring consistent weld quality, these robots reduce rework rates and improve manufacturing performance indicators such as cycle time and defect rate.
Below is a simplified comparison between manual welding and robotic welding in automotive manufacturing:
| Feature | Manual Welding | Robotic Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Weld Consistency | Variable | Highly Consistent |
| Production Speed | Moderate | High |
| Worker Safety Exposure | Higher | Lower |
| Data Monitoring | Limited | Advanced Sensors |
| Integration with AI | Minimal | Supported |
This shift toward automation is strongly linked to broader industrial robotics adoption trends.
Recent Updates and Trends in Robotic Welding
In 2025, automotive manufacturers continue to invest in collaborative robotics, artificial intelligence, and machine vision systems to improve welding accuracy. Over the past year, several trends have shaped car body welding automation:
-
Increased adoption of AI-driven weld inspection systems
-
Expansion of collaborative robots working alongside human operators
-
Greater use of digital twin simulations for production planning
-
Integration of cloud-based manufacturing analytics
-
Rising focus on energy-efficient robotic systems
Companies such as ABB, KUKA, and FANUC have expanded their robotic welding portfolios with improved sensor integration and real-time monitoring capabilities during 2024 and early 2025.
In India, automotive manufacturing hubs in states like Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu are gradually increasing robotic automation in response to rising vehicle production and export demand. Government initiatives promoting advanced manufacturing technologies have also influenced adoption.
One notable trend during 2024–2025 has been the growth of laser welding robots, which provide precise weld seams with minimal heat distortion. This is particularly useful in electric vehicle battery enclosures and lightweight body components.
Laws, Regulations, and Government Programs
Car body welding robots operate within strict industrial safety and manufacturing compliance frameworks. In India, workplace safety and automation practices are influenced by national labor and industrial safety regulations. Compliance includes:
-
Occupational safety standards for factory environments
-
Electrical equipment safety regulations
-
Industrial robot installation guidelines
-
Environmental norms related to welding fumes and emissions
Government programs such as “Make in India” and advanced manufacturing policies encourage modernization of production facilities through industrial automation. These initiatives aim to enhance global competitiveness and manufacturing output.
Internationally, robotic welding systems must comply with safety standards such as ISO 10218 for industrial robots and robotic systems. Automotive manufacturers exporting vehicles must also meet global quality benchmarks, which indirectly support robotic welding adoption.
Environmental regulations also influence welding operations. Energy-efficient robots and emission-reduction technologies are increasingly prioritized to meet sustainability targets.
Tools and Resources for Understanding Robotic Welding
Several tools and digital platforms help professionals understand and evaluate car body welding robots and industrial automation systems.
Helpful tools and resources include:
-
Robotic simulation software for welding path programming
-
Digital twin platforms for factory layout planning
-
Welding quality inspection software with AI analytics
-
Industrial automation certification programs
-
Manufacturing analytics dashboards
Major robotics manufacturers such as Yaskawa Electric provide technical documentation, whitepapers, and product catalogs explaining robotic welding systems.
Educational resources are also available through:
-
Engineering university programs in robotics and automation
-
Industry webinars on smart manufacturing
-
Technical journals focused on industrial automation
-
Automotive engineering standards publications
A simplified example of production performance improvement after robotic integration is shown below:
| Metric | Before Automation | After Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Weld Defect Rate | 4–6% | 1–2% |
| Average Cycle Time | 90 seconds | 55 seconds |
| Worker Exposure to Fumes | High | Significantly Reduced |
| Production Data Tracking | Manual Logs | Real-Time Monitoring |
These improvements demonstrate why robotic welding is considered a core part of smart factory transformation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of welding do car body robots perform?
Car body welding robots commonly perform spot welding, arc welding, and laser welding. Spot welding is widely used for joining sheet metal panels, while laser welding is applied for precision seams and lightweight materials.
Are car body welding robots fully autonomous?
Most robotic welding systems operate within predefined programs and monitored production lines. While automation is high, human technicians supervise operations, perform maintenance, and adjust programming when needed.
How do welding robots improve vehicle safety?
Consistent and precise welds strengthen structural joints in vehicle frames. Stronger weld integrity contributes to improved crash performance and long-term durability of automotive bodies.
Do welding robots replace human workers?
Robotic systems primarily handle repetitive and hazardous tasks. Human workers remain essential for programming, quality control, maintenance, engineering design, and system supervision.
What industries besides automotive use welding robots?
Welding robots are also used in aerospace manufacturing, heavy machinery production, shipbuilding, and industrial equipment fabrication.
Conclusion
Car body welding robots represent a key component of modern automotive manufacturing and industrial automation. By combining robotics engineering, artificial intelligence, and precision welding technology, these systems improve production efficiency, consistency, and workplace safety.
As global demand for electric vehicles and advanced manufacturing grows, robotic welding will continue evolving through smarter software integration and enhanced sensor systems. Regulatory frameworks, sustainability goals, and digital transformation initiatives further shape how these robots are deployed in factories.
Understanding car body welding robots provides insight into the broader shift toward smart factory automation and data-driven manufacturing. For engineers, manufacturing professionals, and industry observers, this topic reflects the future direction of automotive production technology.










